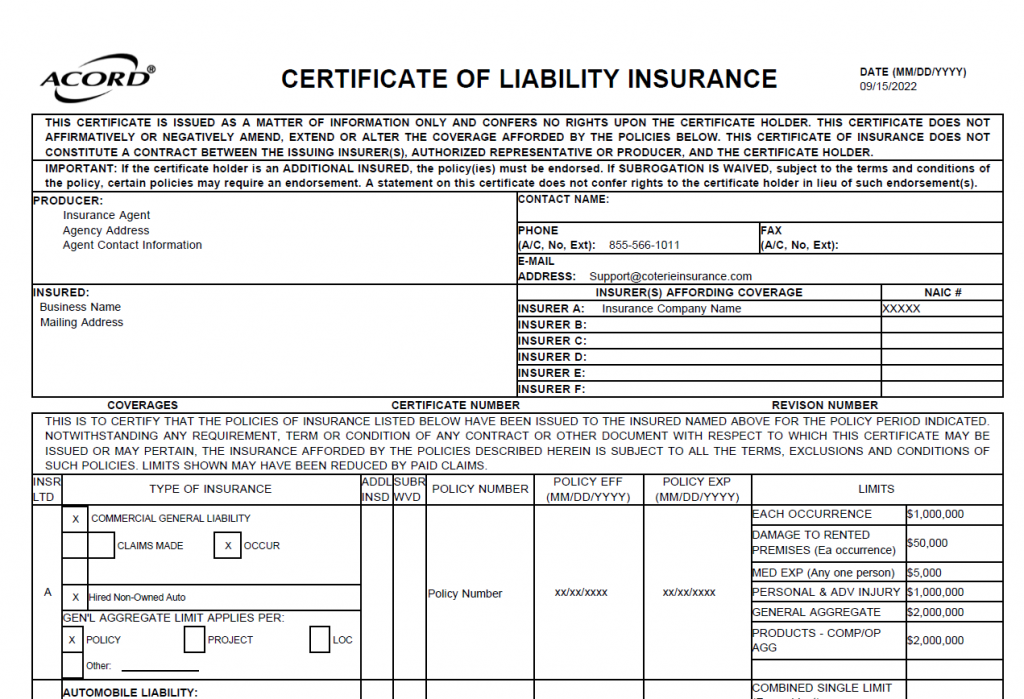
In the complex world of business, insurance certificates play a pivotal role in establishing trust, mitigating risks, and ensuring legal compliance. These documents, which provide proof of coverage, are often a prerequisite for contracts, partnerships, and even participation in certain industries. From general liability to workers’ compensation, understanding the nuances of business insurance certificates is crucial for any organization seeking to operate smoothly and responsibly.
This guide delves into the intricacies of business insurance certificates, exploring their purpose, importance, and the steps involved in obtaining, verifying, and managing them. We’ll also examine the different types of certificates available, legal considerations, and emerging trends that are shaping the future of this critical aspect of business operations.
What is a Business Insurance Certificate?

A business insurance certificate, also known as a certificate of insurance, is a concise document that summarizes the key details of a business’s insurance coverage. It serves as proof of insurance and is typically required by clients, vendors, or landlords to ensure that a business has adequate coverage to protect against potential risks.
Purpose and Significance of a Business Insurance Certificate
A business insurance certificate plays a crucial role in establishing trust and demonstrating financial responsibility. It provides assurance to third parties that the insured business has the necessary insurance coverage to protect them from potential liabilities arising from accidents, injuries, or property damage. For example, a general contractor may require a certificate of insurance from its subcontractors to ensure that it is not held liable for any accidents or injuries that occur on the job site.
Types of Business Insurance Certificates
Business insurance certificates can be issued for various types of insurance coverage, including:
- General Liability Insurance: This coverage protects businesses from financial losses arising from third-party claims related to bodily injury, property damage, or personal injury caused by the business’s operations or products.
- Workers’ Compensation Insurance: This coverage provides benefits to employees who suffer work-related injuries or illnesses. It also protects employers from lawsuits related to employee injuries.
- Property Insurance: This coverage protects businesses from financial losses due to damage or destruction of their property, such as buildings, equipment, or inventory, caused by events like fire, theft, or natural disasters.
Information Included on a Business Insurance Certificate
A typical business insurance certificate includes the following information:
- Policy Number: This unique identifier identifies the specific insurance policy.
- Insurance Company: The name of the insurance company providing coverage.
- Policy Period: The dates when the insurance policy is in effect.
- Insured Parties: The names of the businesses or individuals covered by the policy.
- Coverage Limits: The maximum amount of money the insurance company will pay for a covered claim.
- Deductible: The amount of money the insured party must pay before the insurance company begins to cover the claim.
- Exclusions: Specific events or situations that are not covered by the policy.
- Certificate Holder: The name of the party requesting the certificate.
Why are Business Insurance Certificates Important?

Business insurance certificates are more than just pieces of paper; they serve as crucial documents that demonstrate a business’s commitment to financial responsibility and risk management. These certificates hold significant weight in various legal, contractual, and commercial contexts, playing a vital role in protecting businesses from potential financial losses and liability claims.
Legal and Contractual Requirements
Insurance certificates are often mandated by law or contract, ensuring that businesses meet specific insurance coverage requirements. This is particularly relevant in industries where the potential for risk and liability is high. For example, construction companies may be required to provide certificates demonstrating workers’ compensation coverage to protect their employees. Similarly, businesses renting property may need to show proof of liability insurance to cover potential damages to the leased premises.
Obtaining a Business Insurance Certificate
Securing a business insurance certificate is a straightforward process that involves contacting your insurance provider and providing the necessary information. The certificate serves as a formal document verifying your insurance coverage, offering assurance to your clients, vendors, or other stakeholders.
Requesting a Certificate
The process of obtaining a business insurance certificate typically involves these steps:
- Contacting your insurance agent or broker: Begin by reaching out to your insurance agent or broker, who will guide you through the process and ensure your request is processed efficiently.
- Providing policy details: You will need to provide your insurance policy number, the effective date of your policy, and the type of coverage you require.
- Specifying certificate recipients: Clearly identify the parties to whom you want the certificate to be issued. This could include clients, vendors, landlords, or other stakeholders.
- Submitting the request: Most insurance providers offer online portals or forms for submitting certificate requests. Alternatively, you can request the certificate via email or phone.
Information Required for a Successful Certificate Request
To ensure your request is processed smoothly and efficiently, ensure you provide the following information:
- Policy number: This is a unique identifier for your insurance policy.
- Insured party details: This includes the name of your business, address, and any other relevant details.
- Coverage details: Specify the types of coverage included in your policy, such as general liability, property insurance, or workers’ compensation.
- Certificate recipient information: Provide the name, address, and any other relevant details of the party receiving the certificate.
Verifying the Validity of a Business Insurance Certificate
A business insurance certificate is a crucial document that verifies the existence and coverage of an insurance policy. However, it’s essential to ensure the certificate’s authenticity and validity to avoid potential liabilities and disputes.
Verifying the validity of a business insurance certificate involves several steps to ensure its authenticity and accuracy.
Contacting the Issuing Insurance Company
It’s paramount to contact the issuing insurance company directly to confirm the certificate’s accuracy. This step is crucial for verifying the policy’s coverage details, including the policyholder’s name, policy number, effective dates, and coverage limits.
- Request a copy of the policy itself to compare it with the certificate.
- Verify that the certificate details match the policy information.
- Inquire about any endorsements or modifications made to the policy since the certificate’s issuance.
Identifying Potential Red Flags or Inconsistencies
While contacting the issuing insurance company is the most reliable method for verifying the certificate’s validity, it’s essential to be aware of potential red flags or inconsistencies that may indicate a fraudulent or inaccurate certificate.
- Mismatched information: Check for discrepancies between the certificate and other documents, such as the policyholder’s name, policy number, or coverage details.
- Missing or incomplete information: A certificate lacking essential details like the policyholder’s name, policy number, effective dates, or coverage limits should raise concerns.
- Unusual formatting or logos: Be wary of certificates with unfamiliar formatting or logos that don’t align with the issuing insurance company’s standard branding.
- Suspicious contact information: If the certificate’s contact information seems dubious or doesn’t match the insurance company’s official website, it’s a red flag.
Types of Business Insurance Certificates

A business insurance certificate is a document that summarizes the coverage provided by an insurance policy. These certificates are essential for various business transactions, demonstrating the insured’s financial responsibility and compliance with legal requirements. The types of business insurance certificates available vary depending on the specific risks and needs of the business.
Types of Business Insurance Certificates
Different types of business insurance certificates cater to various risks and needs. Understanding the specific coverage offered by each type is crucial for businesses to choose the appropriate insurance protection.
- General Liability Insurance: This type of insurance protects businesses from financial losses arising from third-party claims of bodily injury or property damage. It covers legal defense costs, settlements, and judgments. General liability insurance is typically required for businesses that interact with the public, such as retail stores, restaurants, and service providers.
- Workers’ Compensation Insurance: This insurance provides coverage for employees who are injured or become ill while performing their job duties. It covers medical expenses, lost wages, and rehabilitation costs. Workers’ compensation insurance is mandatory in most states and is essential for protecting businesses from lawsuits and financial burdens related to workplace injuries.
- Property Insurance: This type of insurance protects businesses from financial losses due to damage or destruction of their property, including buildings, equipment, inventory, and other assets. Property insurance can cover events such as fire, theft, vandalism, and natural disasters.
- Commercial Auto Insurance: This insurance covers businesses for damages or injuries caused by their vehicles. It includes liability coverage for accidents, collision coverage for damage to the insured vehicle, and comprehensive coverage for damage from events like theft or vandalism.
- Professional Liability Insurance (Errors & Omissions): This insurance protects businesses from claims arising from professional negligence, errors, or omissions in their services. It is essential for professionals such as doctors, lawyers, accountants, and consultants.
- Product Liability Insurance: This insurance protects businesses from claims arising from defective products that cause injury or damage. It is essential for businesses that manufacture or sell products.
- Cyber Liability Insurance: This insurance protects businesses from financial losses arising from cyberattacks, data breaches, and other cybersecurity incidents. It covers costs such as data recovery, legal expenses, and regulatory fines.
- Directors and Officers (D&O) Liability Insurance: This insurance protects directors and officers of a company from personal liability for financial losses arising from their decisions or actions while acting in their official capacity.
Categorization of Business Insurance Certificates by Industry
The types of business insurance certificates required can vary significantly depending on the industry or business activity. The following table provides a general overview of common insurance needs for different industries:
| Industry | Common Insurance Certificates |
|---|---|
| Retail | General Liability, Property, Workers’ Compensation, Product Liability |
| Construction | General Liability, Workers’ Compensation, Property, Commercial Auto |
| Healthcare | General Liability, Workers’ Compensation, Professional Liability (Medical Malpractice), Property |
| Technology | General Liability, Workers’ Compensation, Cyber Liability, Professional Liability (Technology Errors & Omissions) |
| Financial Services | General Liability, Workers’ Compensation, Professional Liability (Financial Services Errors & Omissions), D&O Liability |
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Business insurance certificates are not just pieces of paper; they are legal documents with significant implications. Understanding the legal and regulatory framework surrounding these certificates is crucial for businesses, as non-compliance can lead to serious consequences.
Insurance Certificate Requirements
Insurance certificate requirements vary depending on the specific industry, location, and contractual agreements. For example, many states require businesses to provide proof of workers’ compensation insurance before they can operate. Additionally, construction projects often require contractors to provide certificates of liability insurance as a condition of participation.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failure to comply with insurance certificate regulations can result in a range of penalties, including:
- Fines: Regulatory bodies can impose fines for operating without the required insurance or for providing inaccurate or incomplete certificates.
- License Revocation: In some cases, non-compliance with insurance requirements can lead to the suspension or revocation of business licenses.
- Contractual Disputes: If a business fails to provide the required insurance certificates, it may be in breach of contract, potentially leading to legal disputes.
- Liability Exposure: Lack of adequate insurance can leave businesses vulnerable to significant financial losses in the event of an accident or incident.
Examples of Legal Cases
Insurance certificates have played a critical role in numerous legal cases, often serving as evidence in disputes related to:
- Construction Accidents: Certificates of liability insurance are frequently used to determine the extent of coverage in construction accidents, ensuring that injured parties receive compensation.
- Property Damage: In cases of property damage, insurance certificates can help establish the financial responsibility of the parties involved, facilitating settlement negotiations.
- Product Liability: Insurance certificates can provide evidence of product liability coverage, which is essential in cases where defective products cause injury or damage.
Best Practices for Managing Business Insurance Certificates
Effective management of business insurance certificates is crucial for maintaining compliance, minimizing risk, and ensuring smooth operations. A well-organized system helps businesses readily access essential coverage information, avoid potential legal issues, and demonstrate responsible risk management practices.
Storing Business Insurance Certificates
Storing insurance certificates securely and accessibly is paramount. Businesses should adopt a standardized approach to ensure certificates are easily retrievable when needed.
- Digital Storage: Utilizing a cloud-based document management system allows for secure, centralized storage and easy access from any location. This also simplifies sharing certificates with stakeholders.
- Physical Storage: If opting for physical storage, maintain a dedicated, secure location with controlled access, ideally in a fireproof safe. Ensure certificates are organized by policy type, date, and coverage details.
- Version Control: Implement a system to track certificate revisions, ensuring the most up-to-date version is readily available. This prevents relying on outdated information.
Tracking Business Insurance Certificates
Tracking certificates is essential for ensuring compliance and avoiding gaps in coverage.
- Centralized Database: Maintain a comprehensive database that tracks all certificates, including policy details, coverage periods, renewal dates, and relevant contact information. This database serves as a single source of truth for insurance information.
- Automated Reminders: Utilize software tools or calendar reminders to trigger alerts for upcoming renewals, policy expirations, and certificate updates. This helps prevent coverage lapses and ensures timely action.
- Regular Audits: Conduct periodic audits to verify the accuracy and completeness of the certificate database, ensuring it accurately reflects current coverage and policy information.
Updating Business Insurance Certificates
Regularly updating certificates is essential to maintain accurate coverage information and ensure compliance with evolving requirements.
- Renewal Notifications: Promptly respond to renewal notices from insurance providers, ensuring the policy is renewed on time and the new certificate is obtained and stored appropriately.
- Policy Changes: Update certificates immediately after any policy changes, such as additions, deletions, or modifications to coverage. This ensures all stakeholders have access to the latest information.
- Certificate of Insurance Requests: Respond to requests for certificates of insurance promptly and accurately, providing the most up-to-date information to meet the specific requirements of each request.
Illustrative Flowchart for Managing Business Insurance Certificates
A flowchart can visually represent a systematic approach to managing insurance certificates, ensuring efficiency and compliance.
Start
> Receive Insurance Certificate
> Verify Certificate Information
> Store Certificate Digitally or Physically
> Update Certificate Database
> Set Renewal Reminders
> Process Certificate Requests
> Periodically Audit Certificate Database
End
The Future of Business Insurance Certificates
![]()
The landscape of business insurance certificates is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by the convergence of emerging technologies and evolving industry practices. This evolution is poised to reshape how businesses manage and verify insurance coverage, ushering in a new era of efficiency, security, and transparency.
Digital Certificates and Online Verification Platforms
The adoption of digital certificates and online verification platforms is revolutionizing the way businesses manage and share insurance information. These platforms offer several advantages over traditional paper-based certificates:
- Enhanced Security: Digital certificates are inherently more secure than paper certificates, as they are encrypted and tamper-proof, reducing the risk of fraud and forgery.
- Streamlined Verification: Online verification platforms provide instant access to certificate information, eliminating the need for manual verification processes and reducing the time and effort required to confirm insurance coverage.
- Real-time Updates: Digital certificates can be updated in real-time, ensuring that all parties have access to the most current information. This eliminates the risk of relying on outdated or inaccurate data.
- Reduced Costs: By eliminating the need for paper certificates and manual verification processes, digital certificates and online verification platforms can significantly reduce administrative costs.
Examples of online verification platforms include Verisk’s Insurance Services Office (ISO) and Aon’s Riskonnect. These platforms allow businesses to securely share and verify insurance certificates with clients, vendors, and other stakeholders.
Adapting to the Evolving Landscape
Businesses can adapt to these changes and optimize their certificate management practices by embracing the following strategies:
- Adopt Digital Certificates: Transitioning to digital certificates is a crucial step in streamlining certificate management and enhancing security.
- Utilize Online Verification Platforms: Leverage online verification platforms to simplify the process of verifying insurance coverage and ensure that all parties have access to the most up-to-date information.
- Integrate with Existing Systems: Integrate digital certificate and online verification platforms with existing business systems to automate certificate management processes and improve efficiency.
- Train Employees: Provide training to employees on the use of digital certificates and online verification platforms to ensure seamless adoption and effective utilization.
By embracing these strategies, businesses can position themselves to navigate the evolving landscape of business insurance certificates and optimize their risk management practices.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Business insurance certificates play a crucial role in various situations, demonstrating their significance in risk mitigation, dispute resolution, and ensuring business continuity. Examining real-world examples and case studies sheds light on the practical applications and impact of these certificates.
Examples of Business Insurance Certificate Usage
Here are some real-world examples of how business insurance certificates are used in various situations:
- Construction Projects: Before commencing a construction project, general contractors often require subcontractors to provide certificates of insurance. These certificates ensure that subcontractors have the necessary liability coverage, protecting the general contractor from potential claims arising from the subcontractor’s work.
- Event Planning: Event organizers typically require vendors and service providers to provide certificates of insurance to demonstrate financial responsibility. This ensures that the event organizer is protected from potential liability arising from accidents or injuries during the event.
- Leasing Agreements: Landlords often require tenants to provide certificates of insurance as part of a lease agreement. These certificates ensure that the tenant has sufficient liability coverage to protect the landlord from potential claims arising from the tenant’s activities on the leased premises.
Case Studies Illustrating the Importance of Business Insurance Certificates
Case studies provide valuable insights into the real-world impact of business insurance certificates. Here are some examples:
- Dispute Resolution: A construction project was delayed due to a subcontractor’s negligence, resulting in financial losses for the general contractor. The general contractor was able to recover damages from the subcontractor’s insurance company based on the certificate of insurance provided by the subcontractor.
- Risk Mitigation: A company was hosting a large conference at a convention center. The convention center required the company to provide a certificate of insurance demonstrating adequate liability coverage. This ensured that the convention center was protected from potential claims arising from the event.
- Business Continuity: A small business was involved in a car accident while transporting goods for a client. The business was able to continue operations without significant disruption due to the business insurance certificate, which covered property damage and liability claims.
Key Takeaways from Examples and Case Studies
| Scenario | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Construction Project Delays | Certificates of insurance protect general contractors from financial losses due to subcontractor negligence. |
| Event Planning and Liability | Certificates of insurance ensure that event organizers are protected from potential claims arising from accidents or injuries during the event. |
| Leasing Agreements and Landlord Protection | Certificates of insurance provide landlords with assurance that tenants have sufficient liability coverage to protect the landlord from potential claims. |
| Dispute Resolution and Damage Recovery | Certificates of insurance facilitate the resolution of disputes and allow parties to recover damages from the insured party’s insurance company. |
| Risk Mitigation and Event Safety | Certificates of insurance demonstrate financial responsibility and provide assurance to event venues and other stakeholders. |
| Business Continuity and Operational Resilience | Certificates of insurance ensure that businesses can continue operations despite unforeseen events, such as accidents or property damage. |
Closing Summary
As businesses navigate an increasingly complex and interconnected landscape, the importance of business insurance certificates continues to grow. By understanding the intricacies of these documents, businesses can ensure they are adequately protected, meet legal requirements, and establish strong relationships with clients, partners, and vendors. Proactive management of insurance certificates empowers businesses to operate with confidence, knowing they have the necessary coverage in place to weather any storm.